Experience Sharing: Hepatitis C Virus Reflex Testing
A thorough HCV care cascade involves proper screening, confirmation of the presence of HCV RNA, and linking patients to medical care. The multistep testing procedure represents barriers to HCV care. HCV reflex testing is a strategy that simplifies the diagnostic algorithms. Namely, the laboratory performs anti-HCV testing first, if the result is positive, the laboratory will immediately perform an HCV RNA test on the same blood sample. Reflex testing obviates the need for the patient to return for follow-up testing should the initially HCV antibody test be reactive. Implementation of reflex testing enables timely and accurate diagnosis of HCV.
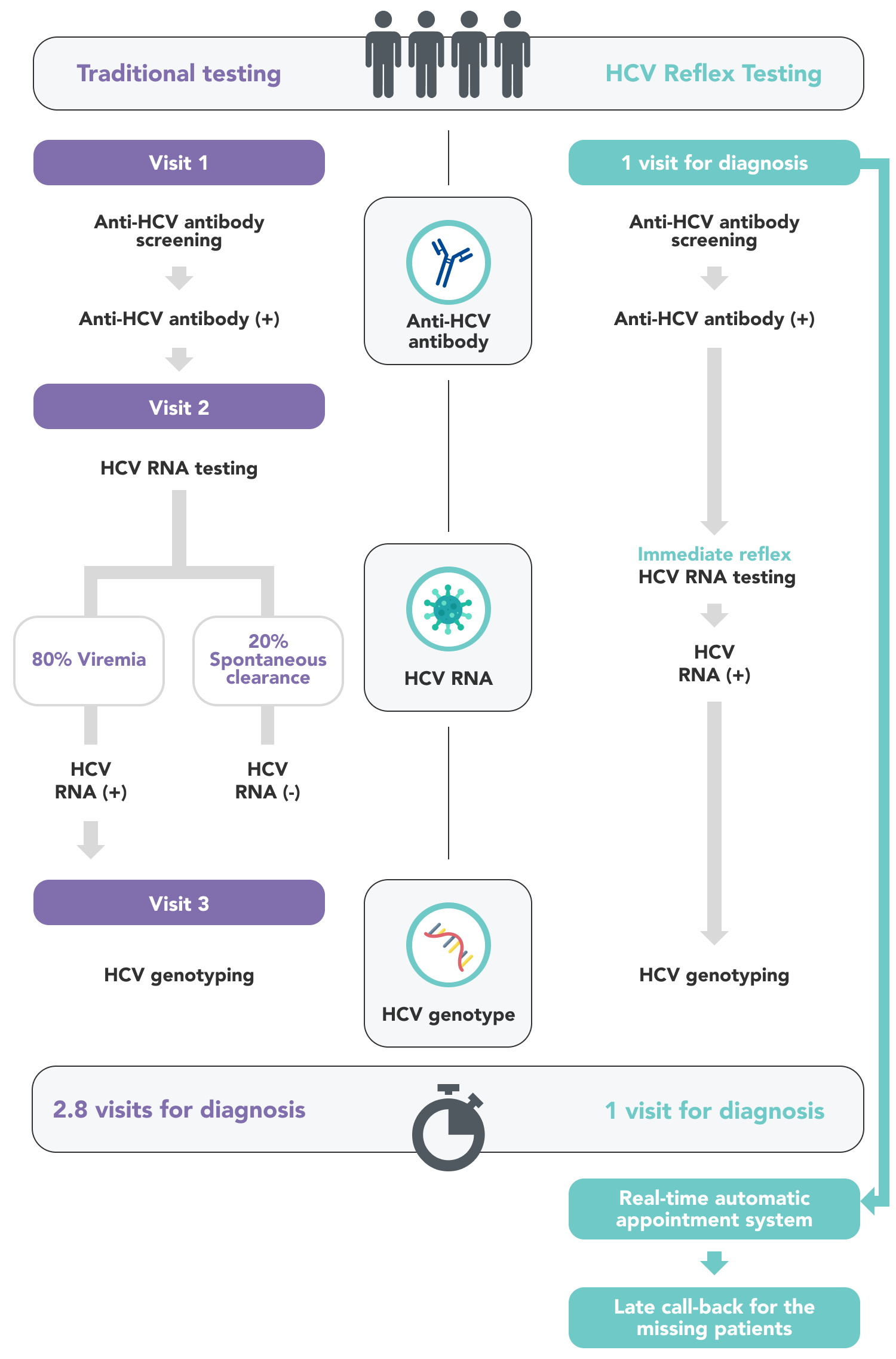
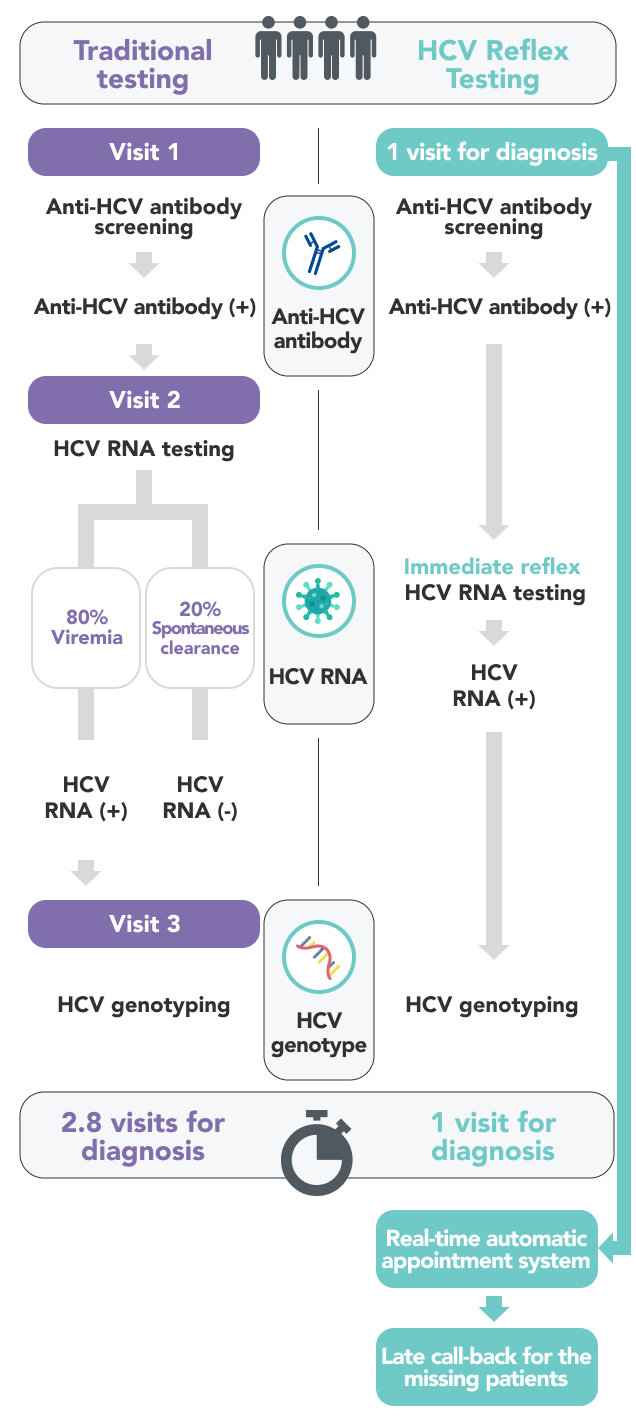
The in-hospital hepatitis C care cascade (R.N.A model) includes serial modalities: (1) HCV reflex testing (increasing timely and accurate diagnosis) (2) Real-time automatic appointments (enhancing accessibility), and (3) Late call-back for the missing patients (raising awareness).
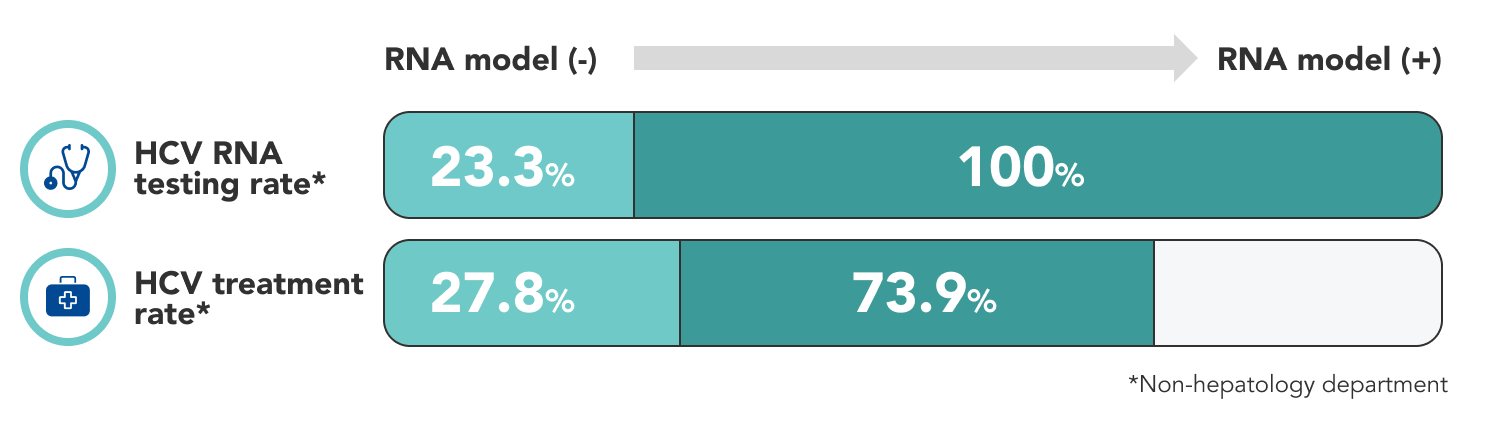
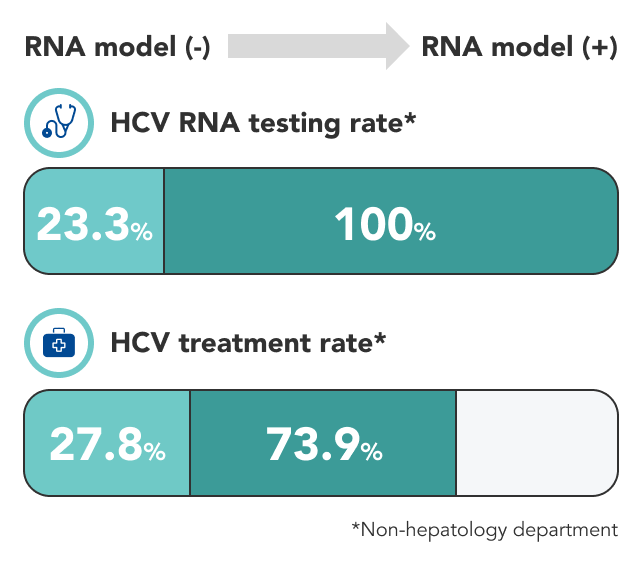
Implementation of R.N.A model is associated with a significant increase in HCV RNA diagnosis and treatment rate for patients from non-hepatology departments. This care cascade successfully increased the treatment update and set up a model for enhancing in-hospital HCV elimination.
-
HCV micro-elimination in prison Outreach onsite treatment with pangenotypic DAA Prisoners are at high risk of HCV infection, with prevalence rates ranging from 3.1% to 38%. Because HCV is readily transmitted through injection drug use, and individuals with substance use disorders are often incarcerated, there is a high prevalence of HCV infection in correctional setting. The anti-HCV prevalence rate could be as high as 91% among incarcerate people who inject drugs (PWID). Therefore, incorporating correctional settings into HCV elimination plans are of importance to reduce the burden of HCV infection.
-
Experience Sharing: HCV‑HELP study Hepatitis C Virus in‑hospital micro elimination program Well-designed strategies can effectively prevent the spread of HCV. Measurements included efficient tests and diagnosis, large-scale screening programs and easily-accessed HCV care cascade.The HCV in-hospital elimination program (HCV-HELP) is to eliminate HCV, reduced hazards and provide a safe hospital environment for public and hospital staff members.
-
Experience Sharing: Micro-elimination of Hepatitis C virus infection in hemodialysis centers (ERASE-C) Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is prevalent in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis and can be attributed to the nosocomial transmission in hemodialysis centers. Due to the highly prevalent and contiguous property in the close-contact environment, and the lack of an available vaccine, the strategy of ‘treatment as prevention’ is imperative for the control of HCV infection in the uremic hemodialysis population. ERASE-C program implements a universal outreach screening strategy, followed by either link-to-care or decentralized on-site treatment in 18 hemodialysis centers, in order to achieve micro-elimination of HCV for uremic patients in hemodialysis centers.
-
Experience Sharing: Hepatitis C Virus Reflex Testing A thorough HCV care cascade involves proper screening, confirmation of the presence of HCV RNA, and linking patients to medical care. The multistep testing procedure represents barriers to HCV care. HCV reflex testing is a strategy that simplifies the diagnostic algorithms. Namely, the laboratory performs anti-HCV testing first, if the result is positive, the laboratory will immediately perform an HCV RNA test on the same blood sample. Reflex testing obviates the need for the patient to return for follow-up testing should the initially HCV antibody test be reactive. Implementation of reflex testing enables timely and accurate diagnosis of HCV.